A comprehensive introduction to diamond grading standards, diamond grading, diamond grading comparison table

Internationally, diamond grades are assessed mainly based on diamond weight, diamond color, diamond clarity, and diamond cut. However, in addition, diamond fluorescence, Milky, Caffeine, etc. are also within the diamond grade classification standards. The price also has a certain impact, the following is a perfect introduction to the diamond grading standards, and a detailed diamond grading table for you.
Diamond is a standardized product. Its value is determined by the diamond grade, namely diamond weight, cut, color and clarity. Only diamonds that have passed the strict 4C standard evaluation know their true value, and GIA is undoubtedly the most authoritative in the world . The diamond grade is diamond 4C, and the following is the standard for diamond grading.
Weight (Carat)
Diamond weight is calculated in carats (CT). 1 carat = 0.2 grams = 100 points. 0.75 carats is also called 75 points. The value of diamonds shows an irregular geometric progression as the weight of diamonds increases, and consumers can determine it according to their personal preferences and purchasing power. Generally speaking, only diamonds weighing more than 50 points begin to have collection and investment value. The following is a table of diameters corresponding to different sizes of diamonds:
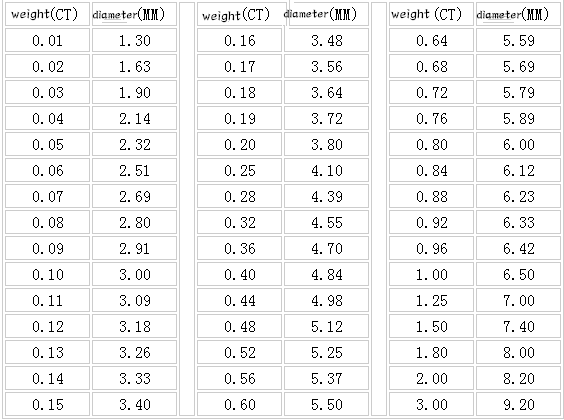

Diamond weight grade
Clarity
Diamond clarity refers to how much the diamond contains. Most of the diamonds on the market contain extremely small, uncrystallized fine carbon materials. The smaller the number and volume of the inclusions, the better the quality. Diamonds with such clarity are rarer, so the price is also lower. not cheap. Internationally, diamond clarity grades are divided into six major categories, namely FL, IF, VVS, VS, SI, I, and can be subdivided into several small grades.
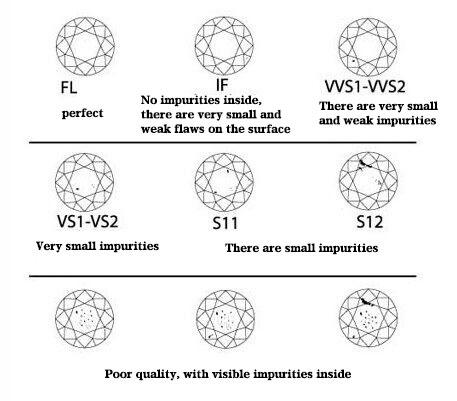
FL means that the diamond is clean under a 10x magnifying glass, that is, there are no inclusions inside and outside the gem.
IF means that there are no flaws inside the diamond under a 10x magnifying glass, but there may be a little flaw on the surface, which can be removed by polishing.
VVS means that the pavilion or surface of the diamond can be seen with very small flaws when observed under a 10x gem magnifying glass. The difference between VVS1 and VVS2 is that the latter has tiny cotton-like dots and small stubble.
VS refers to the very small flaws that can be seen when observing the diamond under a 10x gem magnifying glass. The difference between VS1 and VS2 is that the latter may have tiny cotton spots or stubble.
SI means that it is easy to see flaws when observing a diamond under a 10x magnifying glass, but it is invisible to the naked eye.
I1, I2, and I3 mean that small flaws are easy to see when the diamond is observed under a 10x magnifying glass. The naked eye can just see it easily with the naked eye, and some have obvious cleavage and cracks.
All diamonds use a 10x magnifying glass to observe the clarity, and only I3 grade can easily see the flaws with the naked eye.




Color
The color of common diamonds ranges from completely colorless to yellow and brown. Among them, completely colorless diamonds are very rare and are the highest color grade of common diamonds. According to the purity of the color, the color grade of diamonds is divided into English letters in the world, starting from D, it is divided into D, E, F, G, H, I, J, K, L, M, N… the grades decrease in order .
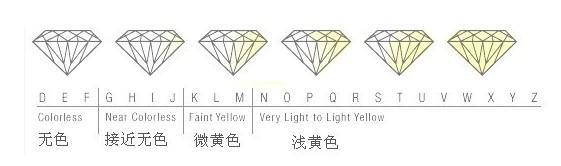
D grade: completely colorless. The highest color level, extremely rare!
E grade: colorless. Only gem identification experts can detect traces of color. It’s a very rare diamond
F grade: colorless. A small amount of color can only be detected by jewelry experts, but it is still considered colorless. Belongs to high-quality diamonds.
G-H grade: nearly colorless. When compared with higher color diamonds, there is a slight color. But diamonds of this color class still have a high value.
I-J grade: close to colorless. A slight color can be detected. The value is higher.
K-M grade: darker color, poor fire color.
N-Z grade: darker color, poor fire color.



Cut
Diamond cut is the only parameter that can be manually controlled in the diamond grade. The quality of the diamond cut determines the presentation of the diamond’s brilliance. A good cut can even cover up the flaws and deficiencies of the diamond itself, so many consumers cut the diamond. Work is the primary focus of buying diamonds. The cut grades of diamonds are divided into excellent cut, very good cut, good cut, normal cut and poor cut.
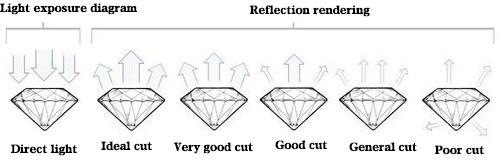
EXCELLENT: represents a standard that only 3% of first-class high-quality diamonds can achieve. This cut makes the diamond reflect almost all light entering the diamond. It is an elegant and outstanding cut.
VERY GOOD: Represents about 15% of diamond cuts. It can make the diamond reflect the light of standard grade cut, but the price is slightly lower.
GOOD: Represents about 25% of diamond cuts. The diamond reflects most of the light entering the diamond. Much cheaper than VG grade.
FAIR: represents about 35% of diamond cuts, which are still high-quality diamonds, but the light reflected by diamonds with general cuts is not as good as that of G-level cuts.
POOR: This includes all diamonds that do not meet general cut standards. The cuts of these diamonds are either deep and narrow or shallow and wide, which tends to allow light to escape from the edges or bottom, thereby making the diamond lose its luster.

Fluorescence Intensity
35% of the diamonds in the world have a fluorescent effect, and 97% of the fluorescent diamonds emit blue fluorescence, occupying the majority, and the remaining 3% are yellow, green, red, and between them. The transitional color fluorescence, such as orange, blue-green, pink, etc. Fluorescence has no effect on the diamond itself, but in some cases it can affect the visual effect of the diamond.
The intensity level of fluorescence is divided into four levels: “very strong”, “strong”, “medium”, “weak” and “none”. When the fluorescence level is at the “medium” or “strong” level, the diamond’s fluorescence will give Diamonds add a hazy or greasy feeling, making the surface of nearly colorless diamonds look whiter, and the price of diamonds with intermediate or higher fluorescence is lower than other diamonds.

Diamond Milk Caffeine
Milk is a cloud-like aggregate of different colors in diamonds, often white, but there is no shortage of gray and black. The white one is usually called “milk”. Its technical term is “clouds”, which affects the clarity and color of the diamond.
Caffeine is an abbreviation of coffee color, brown (or brown). Coffee color often appears as a secondary color in the main colors of yellow, orange, green, pink, and red. In addition to brown in brown colored diamonds, which is a beneficial color, other colors include Cape color diamonds. The middle colors are harmful colors, which will seriously reduce the purity and brightness of the main colors.

The above is an introduction to each level. Buying a diamond is a question that needs to be considered comprehensively, and there are also personal preferences. But the only purpose is to spend the least amount of money to buy the most suitable diamond, but diamonds are luxury goods after all, and they will not depreciate in the current situation. What I want to explain here is that generally only high-grade diamonds above 50 points have the meaning of preservation! The above is the latest content of the diamond grade and diamond grade comparison table, consumers can check their seats!